
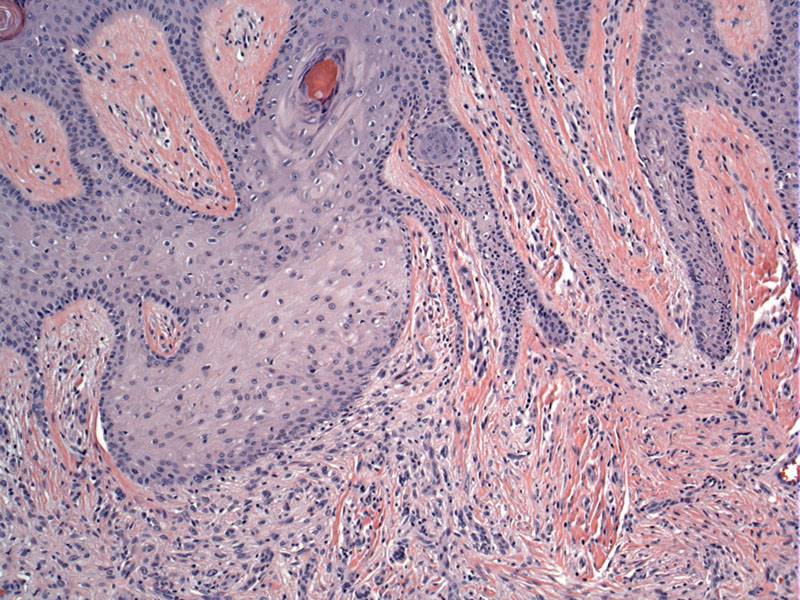
Case 1 - Hyperplasia of overlying epidermis is present which is typical for this lesion. The rete ridges are sometimes described as flattened and table-like with basilar hyperpigmentation, although this is not entirely obvious here.
A proliferation of spindle cells is classically arranged in a storiform or pinwheel-like pattern. The fibroblastic cells have a spindled and somewhat epithelioid appearance.
Ropes of collagen are admixed with the spindle cells, so-called collagen trapping, a helpful feature in diagnosing this entity.
Case 2 - This different case has a more sclerotic appearance. The spindle cells are more angulated and boomerang shaped.
Giant cells can be appreciated. Other than spindle cells, other cell types such as foamy histiocytes, giant cells and hemosiderin-lade macrophages are common in dermatofibromas.
Case 3: Yet another example demonstrating that the overlying epidermis is often hyperplastic.
A closer look at the collagen trapping, forming so-called collagen donuts surrounded by spindle cells.
Dermatofibroma (a.k.a. benign fibrous histiocytoma) is a benign tumor composed of spindled dermal fibroblasts, which may differentiate toward myofibroblasts or histiofibroblasts (Busam). Some authors feel that dermatofibroma is better described as a fibrosing dermatitis rather than a neoplasm.
Histologically, the lesion is a symmetrial proliferation of spindle cells in the dermis. The overlying epidermis is hyperplastic, in some cases with flattened or "tabled" rete ridges. The basal layer is often hyperpigmented. The dermis displays a poorly circumscribed proliferation of spindled fibroblasts and histiocytes arranged in a whorling or storiform pattern. Sometimes, it has been described as a "bomb being dropped in the dermis" (Rapini). Keloidal collagen can be seen at the periphery of the lesion, surrounded by fibroblasts "collagen trapping". Scattered about are multinucleated giant cells, Touton giant cells and foamy histiocytes. Hemosiderin deposition can be quite prominent.
In terms of IHC, factor XIIIa will highlight the dendritic cells. Foamy histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells will be positive for CD68. The myofibroblastic cells will be positive for smooth muscle actin. In contrast to dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, CD34 is negative in dermatofibroma (Busam, Fletcher).
Commonly seen as a brownish nodule on the legs. Other sites include upper extremities and torso. When you pinch the nodule between your fingers and inwardly compress it, it displays a so-called "dimple sign".
Benign; excision is curative in most instances. Exceptionally, metastasis to regional lymph nodes and lung have been reported (Fletcher).
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is CD 34 positive, but this marker is negative in dermatofibroma.
Busam KJ. Dermatopathology: Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology 1st Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2010: 499.
Fletcher CDM, ed. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2007: 1485.
Rapini RP.Practical Dermatopathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2005: 341-2.
