
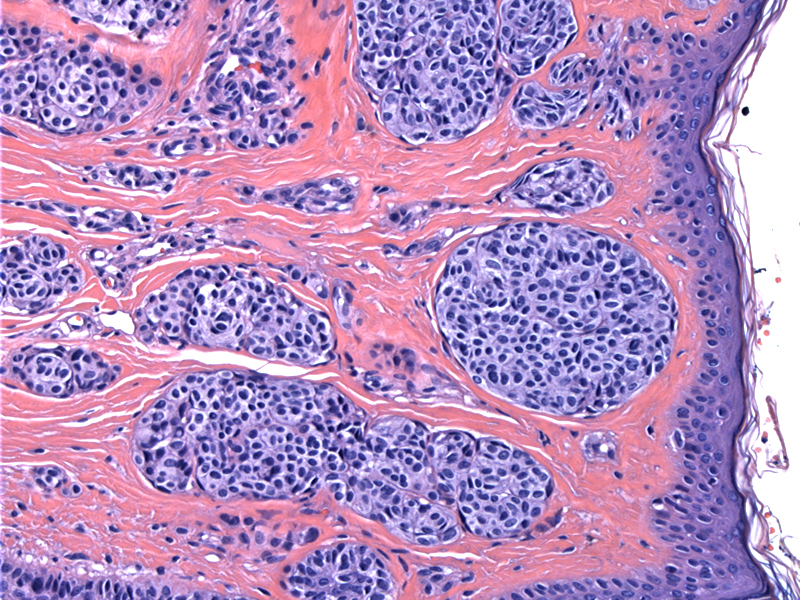
Nests of darkly staining nevomelanocytes within the dermis; there is no junctional activity.
The type B melanocytes (resembling lymphcytes) have minimal cytoplasm and slightly irregular nuclei. There is no pigmentation.
The maturing deep front shows some collagen accumulation, and the nevomelanocytes become smaller with less cytoplasm with progressive descent into the dermis, as well as spindling (type C morphology).
Melanocytic nevus, also known as a "mole", have many variants and descriptions. Intradermal nevus have melanocytic nests located entirely within the dermis whereas junctional nevus have melanocytic proliferations limited to the dermal-epidermal junction. Compound nevus have nests located both in the dermal-epidermal junction and dermia.
These nevi are typically less than 1 cm in diameter, with smooth regular borders.
Rapini RP.Practical Dermatopathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2005: 263.