
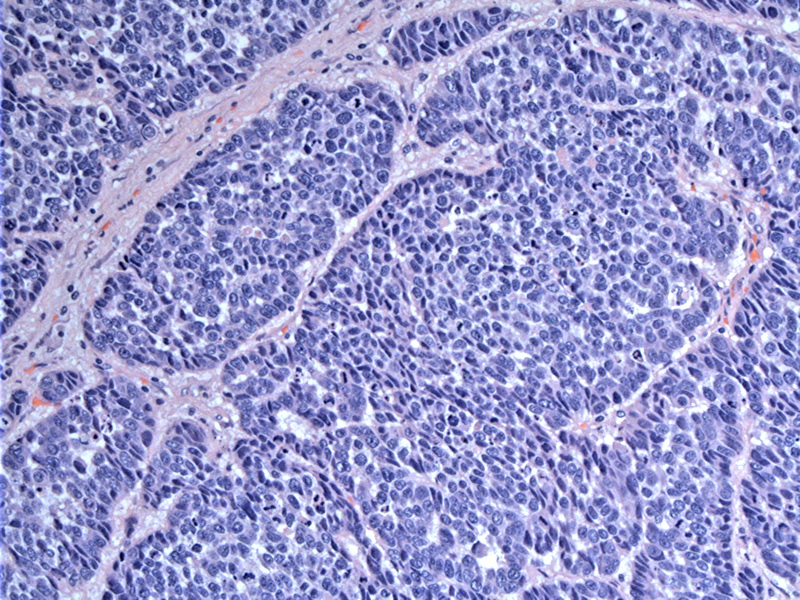
This tumor from a 28 year old female was ER, PR and Her2 negative. Note the lobules composed of sheet-like growth of tumor cells with scant intervening stroma.
Marked cellular pleomorphism, a high N/C ratio, vesicular chromatin with prominent nucleoli are all features of this tumor type. Punctate necrosis is present.
Basal-like carcinomas are also characterized by the presence of metaplastic elements, in this case, in the form of squamous and spindle cells.
The border is pushing and expansile, characteristic of this tumor type.
Extensive geographic necrosis, high mitotic activity, and frequent apoptotic cells are also common.
Synytical growth of tumor cells with scant stroma is typical.
Spindled areas may be encountered.
In terms of treatment, oncologists separate breast cancers into 3 categories: (1) those with hormone receptors responsive to ER-targeted therapy; (2) those with Her2 overexpression receptive to trastuzumab; (3) those that are negative for ER, PR and Her2 overexpression i.e. "triple-negative" cancers.
A note on basal-like carcinomas, triple-negative carcinomas, medullary carcinomas, metaplastic carcinomas and BRCA1:
There is a relationship between all of the above entities, the details of which is beyond this discussion (or my understanding). Suffice to say that basal-like carcinomas, medullary carcinomas, metaplastic carcinomas and BRCA1 (familial) breast cancers are often "triple negative" cancers.
Basal-like cancers exhibit a basal/myoepithelial phenotype (versus a luminal phenotype like the majority of breast cancers). Specifically, basal-like cancers will stain with basal cytokeratins (e.g. CK5/6, CK14, CK17) and myoepithelial markers (e.g. SMA, p63, CD10)(Irvin). Many also express EGFR. Morphological features of basal-like cancers include high grade cytology, syncytial growth, pushing borders and a lymphocytic infiltrate. Again, to emphasize the relationship between the above entities, >90% of metaplastic breast cancers and the majority of medullary carcinomas are basal-like carcinomas (Reis-Filho).
Both basal-like and triple-negative breast cacners tend to affect younger women (<50) and have a higher incidence in African Americans (Reis-Filho).
Breast cancers arising in carriers of germ-line BRCA1 mutations are predominately of basal-like and triple-negative type, suggesting that BRCA1 dysfunction may play a role in the pathogenesis of sporadic basal-like and triple negative cancers.
Basal-like and triple negative cancers are associated with a more aggressive course and a poor prognosis with an increased rate of relapse and metastases. The exception is medullary carcinoma, which may have an improved prognosis, however, the criteria to diagnose medullary carcinoma reproducibly is under investigation.
→Triple negative carcinomas tend to exhibit a basal-like phenotype, but the two are not synonymous.
→Medullary carcinomas, metaplastic carcinomas and carcinomas arising in BRCA1 patients are also triple negative and basal-like.
→These tumors are still under investigation and tend to affect younger women and have a more aggressive course. The exception may be medullary carcinoma.
• Invasive Carcinoma - Special Types : Medullary Carcinoma
Irvin WJ, Carey LA. What is triple-negative breast cancer? Eur J Cancer 2008 (44) 2799-2805.
Reis-Filho JS, Tutt ANJ. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology 2008, 52, 108-118.
