
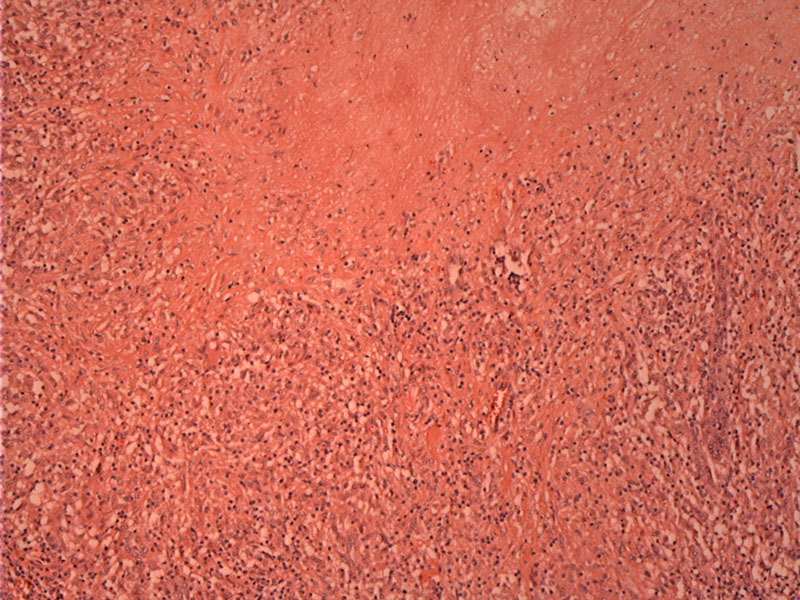
The kidney is heavily involved by foci of coagulative necrosis surrounded by epithelioid histiocytes and lymphocytes.
Coalesced epithelioid granulomas with surround lymphoid inflammation engulfing the few remaining tubules present; significant renal destruction is therefore apparent.
Two normal glomeruli are present within a brisk mixed inflammatory reaction which includes frequent large multinucleated giant cells.
Urogenital tuberculosis develops in 2–20% of individuals with pulmonary disease (Shuberyt; Flechner). Urogenital is the second most common extrapulmonary manifestation of TB following peripheral lymphadenopathy (Wise).
The latent period between pulmonary infection with bacillemia and clinical urological TB averages 22 years (Figueiredo). Because of its insidious evolution and late-onset symptoms, diagnosis and treatment are delayed, resulting in urogenital organ destruction and renal failure. However, patients from developed countries seem to demonstrate a more benign course with few cases of renal failure or kidneys lost (Ferrie).
Symptoms of renal TB include hematuria and pyuria. Routine urine analysis and culture will not identify the true organism (M. tuberculosis), thus, clinical suspicion must remain high for at risk patients. If untreated, pyelonephritis, calculi formation and renal failure may ensue (Wise).
In one metaanalysis, 26.9% of patients developed a non-functioning unilateral kidney and in 7.4%, renal failure (Figueiredo). The infection may descend to involve the ureters and bladder.
Ferrie BG, Rundle JSH. Genito-urinary tuberculosis in Glasgow 1970 to 1979: a review of 230 patients. Scott. Med. J. 1985; 30: 30–4.
Flechner SM, Gow JG. Role of nephrectomy in the treatment of non-functioning or very poorly functioning unilateral tuberculous kidney. J. Urol. 1980; 123: 822–5.
Figueiredo AA, et al. Epidemiology of urogenital tuberculosis worldwide. Int J Urol. 2008 Sep;15(9):827-32.
Schubert GE, Haltaufderheide T, Golz R. Frequency of urogenital tuberculosis in an unselected autopsy series from 1928 to 1949 and 1976 to 1989. Eur. Urol. 1992; 21: 216–23.
Wise GJ, Marella VK. Genitourinary manifestations of tuberculosis. Urol Clin N Am 30(2003) 111-121.