
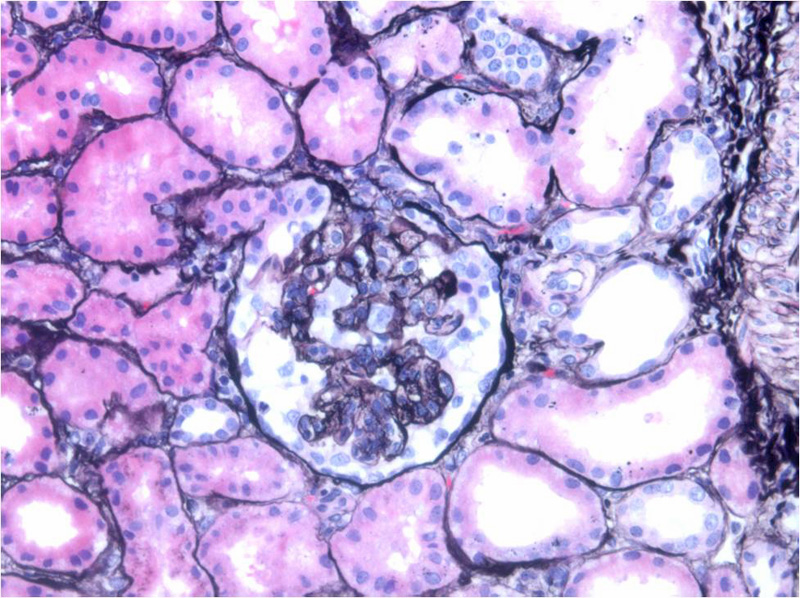
Collapsing FSGS is characterized by collapse of glomerular capillary loops that is segmental or even global (involves the entire glomerulus). The capillary lumens are obliterated. There is hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the overlying podocytes, forming a pseudocrescent.
The hyperplastic epithelial cells (surrounding the glomerular tuft) contain protein droplets which can be seen as pink splotches. Although not obvious in this image, the tubules are often dilated and cystic, containing proteinaceous casts. Interstitial inflammation (lymphocytes, monocytes, plasma cells) is also characteristic.
Collapsing glomerulopathy (CGP) is considered a variant of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). This entity was first described in HIV patients and is also seen in IV drug users. Idiopathic forms of CGP exist and cases of CGP have been reported in association with autoimmune diseases, use of certain medications (interferon, pamidronate), myeloma and renal transplants. CGP tends to have a slight predilection for the male gender and African-Americans.
Compared to the other variants of FSGS, the tubulointerstitial injury is more severe. Acute tubular injury, dilatation of tubules containing eosinophilic proteinaceous casts, interstitial inflammation, interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy can be seen throughout the entire renal parenchyma (Zhou, Rosai). Of note, a particular type of endothelial tubuloreticular inclusion, best demonstrated on electron microscopy, is found in 90% of HIV associated CGP and not present in the other forms of FSGS. These inclusions, however, are not specific and can also be seen in SLE or patients on interferon therapy (Kumar, Rosai).
Rapid renal failure (rapid increase in creatinine) is seen. This collapsing variant of FSGS seen in up to 85% of HIV patients.
Prognosis is much worse than the other two variants (perihilar and glomerular tip lesion). There is poor response to therapy and patients quickly progress to end stage renal failure.
Associated with HIV and IV drug use.
Global and segmental collapse of glomerular tuft is seen with overlying podocyte hyperplasia.
The inflammation and damage to surrounding kidney parenchyma is more severe than that seen in other variants of FSGS.
• Kidney : Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis, Glomerular tip lesion
• Kidney : Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 7th Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2005: 962-4.
Rosai, J. Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology. 9th Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2004: 1171-3.
Zhou M, Magi-Galluzzi, C. Genitourinary Pathology: Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elvesier; 2006: 354-8.