System: Skin: Epidermis: Autoimmune: Pemphigus Vulgaris

System: Skin: Epidermis: Autoimmune: Pemphigus Vulgaris


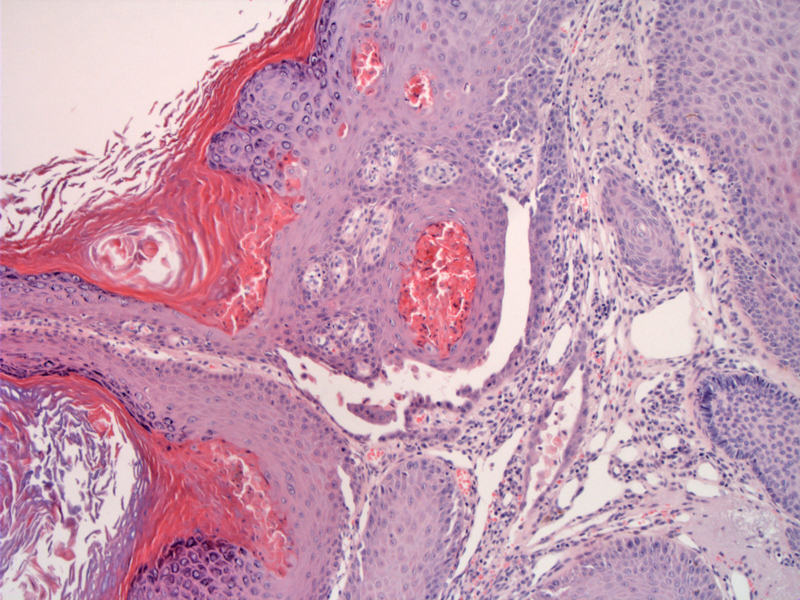
Case 1: Pemphigus vulgaris lesions can occur in the mucosa (usually oral) or on the skin. In this case, this is a cutaneous lesion with a granular layer and hyperkeratosis. Note the characteristic suprabasilar split.
The suprabasilar split leads to a so-called tombstone basal layer.
Direct immunofluorescence shows IgG deposition in a chicken-wire pattern.
The word pemphigus comes from pemphix, the Greek word for blister or bubble. Pemphigus is used to describe a group of autoimmune blistering diseases characterized by intraepidermal blisters/vesicles and circulating autoantibodies that bind to proteins on the cell surface of keratinocytes. There are three main entities: pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus foliaceus and paraneoplastic pemphigus. Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is by far the most common entity of this group and accounts for ~70% of pemphigus cases (Bassam), and the rest of this discussion will focus on PV.
On direct IF with IgG and C3, one would see a "Swiss cheese pattern", meaning that the staining will centered on the intercellular spaces.
Pemphigus vulgaris versus bullous pemphigoid: Just because these two entities often confuses me, I shall briefly compare and contrast them. In pemphigus vulgaris, autoantibodies are directed against cell surface adhesion molecules desmoglein 1 and 3, and thus, IF leads to staining around the keratinocytes, creating a net-like or "swiss-cheese" plattern. On histology, there is a suprabasilar split of the epidermis with acantholysis. In contrast, bullous pemphigoid is due to autoantibodies to the hemidesmosome complex of basement membrane, specifically, to BP1 and BP2 antigen. On IF, one would see a linear deposition of IgG and complement along the basement membrane. On histology, there is a subepidermal split with eosinophils.
Pemphigus vulgaris can arise in the mucous membranes (usually oral cavity) and skin. Usually, mucosal lesions occur before cutaneous lesions. The mouth will have erosions and ulcers, and there would be flaccid fragile vesicles on the skin.
Prior to immunosuppressive therapy, the prognosis was grim, however, these days, the patients can be properly managed with medications.
• Oral Cavity : Pemphigus Vulgaris
• Epidermis : Bullous Pemphigoid
Bassam Z. Pemphigus Vulgaris: eMedicine. Last updated: July 28th 2011. Available at: emedicine.medscape.com/article/1064187-overview
Rapini RP.Practical Dermatopathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2005: 86-7.