
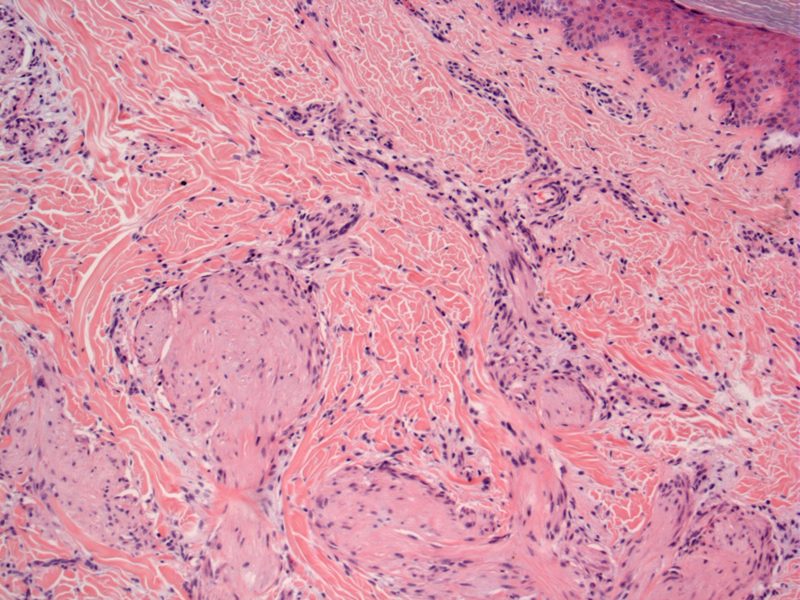
There is a plexiform (multinodular) and infiltrative arrangement of cells at the dermal/subcutaneous junction.
This fibroblastic subtype is composed mainly of elongated clusters and short fascicles of spindle fibroblast-like cells. Cellular atypia is minimal. On the basis of this morphology, the differential diagnoses of may include neurofibroma, plexiform schwannoma, cellular neurothekeoma, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and myofibromatosis.
There is an irregular and infiltrative border with normal fat; mitotic rates are uniformly low in this lesion. This correlates with the poorly circumscribed gross nature of the lesions.
Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor is an uncommon mesenchymal tumor, mostly affecting children and young adults (median age of 14.5 years). It is considered to be of intermediate malignancy as a subset of tumors may metastasize to lymph nodes or lungs (Taher).
Histologically, PHT is composed of multiple small nodules arranged in a multinodular/plexiform pattern. There are spindled fibroblast-like cells, histiocyte-like cells and osteoclast-like giant cells. Two histological patterns have been described: (1) a fibrohistiocytic type composed of histiocyte-like cells and multinucleated giant cells and (2) a fibroblastic subtype composed of elongated clusters as well as fascicles of spindle fibroblast-like cells.
The histocyte-like cells are reactive for CD68 and the fibroblast-like cells are positive for vimentin as well as focally positive for SMA (Taher).
Strong female predilection (6:1). The lesion tends to arise more frequently in children, adolescents, and young adults -- presenting as a slow growing mass in the dermis and subcutis. There is preferential involvement of the upper extremity (64%), especially the fingers, hand, or wrist (45%)(Remstein).
A small percentage may recur and some may even metastasize, most often to the lungs.
Moosavi C, Jha P, Fanburg-Smith JC. An update on plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor and addition of 66 new cases from the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, in honor of Franz M. Enzinger, MD. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2007 Oct;11(5):313-9.
Remstein ED, Arndt CA, Nascimento AG. Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: clinicopathologic analysis of 22 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999 Jun;23(6):662-70.
Taher A, Pushpanathan C. Plexiform Fibrohistiocytic Tumor: A Brief Review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131-1135-1138.