
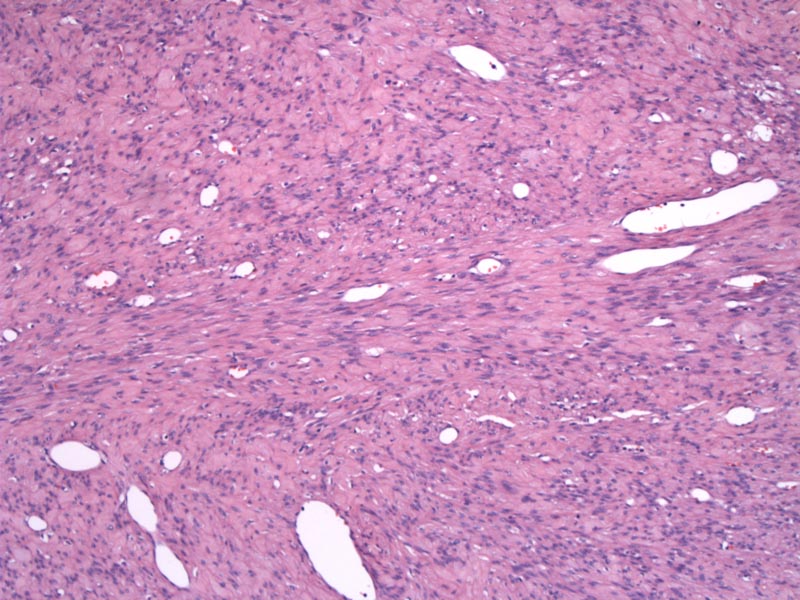
Alternating zones of cellularity are a key feature of AMF. Although not plainly obvious in this particular case, one can still see areas of increased cellularity separated by zones of hypocellularity.
Thin-walled vessels of varying sizes are surrounded by myofibroblasts -- the stromal cells have a tendency to congregate around the vessels.
Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMF) is a benign tumor that occurs in the vulvovaginal region of mainly reproductive age women, and rarely in the inguinoscrotal region of men. Grossly, the tumor is well-circumscribed, rubbery and small (less than 5 cm). Microscopically, AMF is composed of a combination of small to medium-sized thin-walled vessels and a loose edematous stroma with alternating zones of cellularity. The desmin-positive stromal cells are spindled to ovoid, but may be epithelioid.1
The most important entity to rule out is deep (aggressive) angiomyxoma, which will recur locally and may be infiltrating and destructive. Compared to AMF, deep angiomyxoma is poorly circumscribed, and microscopically, the vessels are often medium-sized with thick walls. The stromal is loose, edematous, hypocellular and does not display the alternating zones of cellularity typical of AMF.1,2
This alternating hypocelluarity is also helpful in distinguishing AMF from superficial angiomyxoma, which is grossly lobulated and hypocellular microscopically. Superficial angiomyxomas may also recur locally, but will not be destructive. Note that the stromal cells in superficial angiomyxomas are desmin-negative, compared to desmin-positive stromal cells in AMF and deep angiomyxomas.2
The tumor tends to be small (less than 5 cm) and circumscribed and may be mistaken for a cyst during a clinical exam.
Local excision with adequate margins is sufficient as these tumors do not recur.
Excellent; with clean margins, these neoplasms do not recur.
• Vulva : Cellular Angiofibroma
• Vulva : Deep (Aggressive) Angiomyxoma
• Vulva : Superficial Angiomyxoma
1 Fletcher CDM, ed. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2007: 740.
2 Nucci MR, Oliva Esther. Gynecologic Pathology: Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier: 34-5.