System: Genitourinary: Kidney: Neoplastic: Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma with Focal Oncocytoma

System: Genitourinary: Kidney: Neoplastic: Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma with Focal Oncocytoma


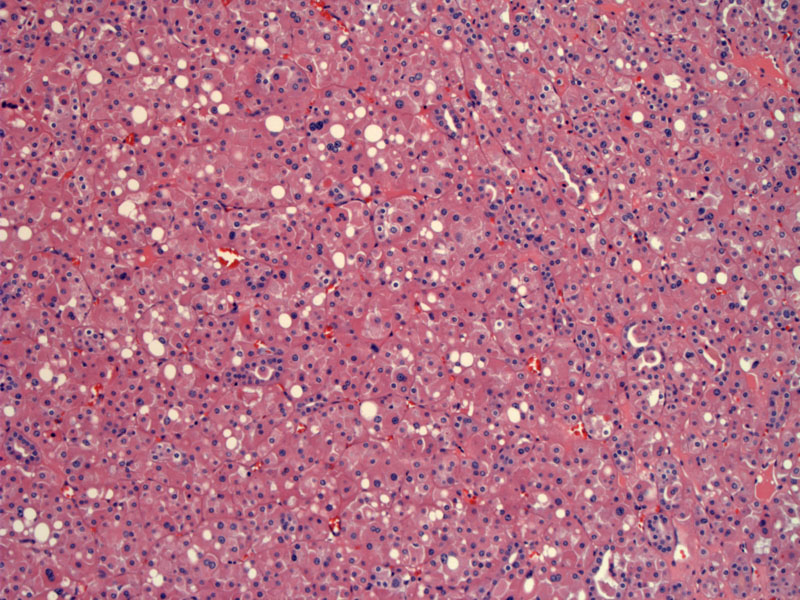
The eosinophilic variant of chromophobe RCC comprises most of the tumor.
Here is a focal transition to an area more compatible with oncocytoma, consisting of packets of cells and edematous stroma, with smaller and more uniform nuclei.
Strong EMA in the chromophobe area is lost in the oncocytoma focus. However, as a significant percentage (up to 45%) of oncocytomas can also stain with EMA, it is not necessary the best differentiating marker.
Cytokeratin 7 is differentially expressed, strongly positive in chromophobe and weak/absent in oncocytoma.
CD10 shows largely absent staining in the oncycytoma areas and positivity in the chromophobe areas.
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (~5% of RCCs) have categorized into two types: (1) classic variant with flocculuent cytoplasm, prominent cytoplasmic membranes, thick walled blood vessels (2) eosinophilic variant with pink granular cytoplasm in addition to other features of chromophobe RCC. Both chromophobe variants exhibit variable cell size and will stain with Hale's colloidal iron. The flocculent cytoplasm is due to the presence of numerous vesicles in the cytoplasm.
The eosinophilic variant can be difficult to distinguish from oncocytoma. Some morphologic clues include a more uniform appearance of cells in oncotyoma whereas chromophobe renal cell carcinomas has more size and shape variation of cells as well as more wrinkling of nuclei.
Key IHC markers to differentiated chromophobe RCC from oncocytoma include CK7 (positive in chromophobe, negative in oncocytoma) and Hale's colloidal iron (positive in chromophobe and negative in oncocytoma).
• Kidney : Renal Cell Carcinoma, Chromophobe Type