
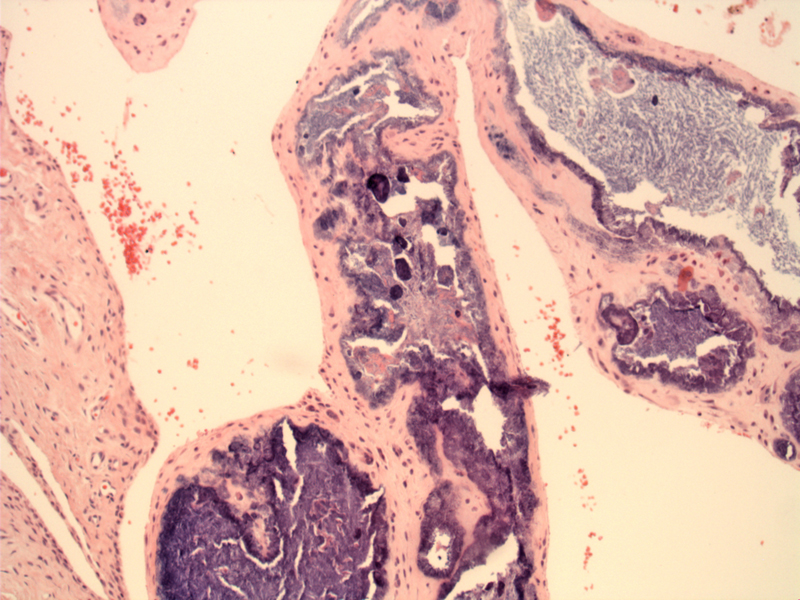
Pseudogout crystal deposition around joint spaces consists of dense deposits of calcium pyrophosphate. Such an appearance has been referred to as "chondrocalcinosis".
Deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals around joint spaces results in joint inflammation and arthritis.
Pseudogout is more common with aging, and may be precipitated by dehydration. It is also associated with hyperparathyroidism, hemochromatosis, and hemophilia. Occasionally true gout may be seen in the same patient with pseudogout.
Ice, NSAIDs, and sometimes aspiration to remove the crystals in the fluid accumulation.