
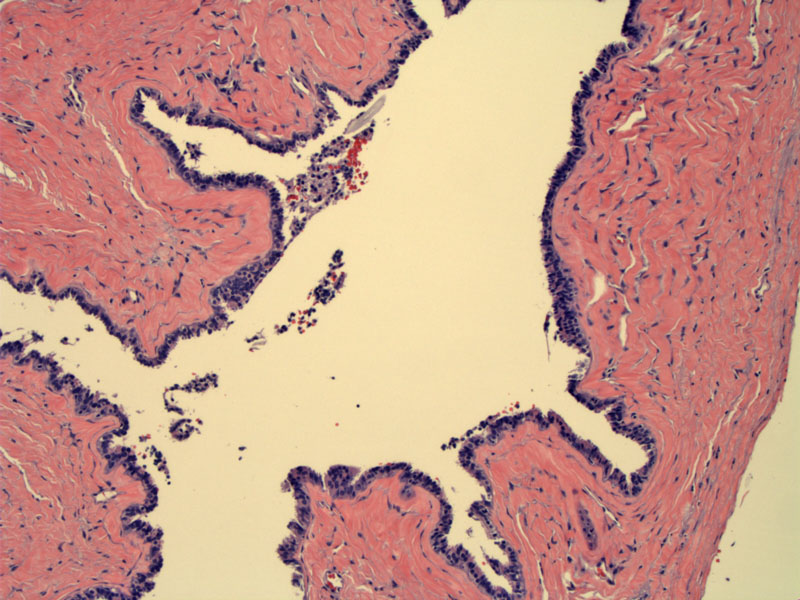
A simple cyst lining consisting of tubal-type epithelium (ciliated and peg cells) is seen here. Branched folds are similar to plicae seen in the fallopian tube. This is consistent with a paramesonephric cyst.
Cilia are evident on the luminal aspect of the epithelium.
Paratubual cysts are derived from either Mullerian (paramesonephric) or Wolffian (mesonephric) remnants. Distinguishing between the two types is not always possible, however, the general features of each are described below.
Mesonephric ducts persists in the female genital tract as a vestigial tubular structures located between the fallopian tube and ovary. The tubules course medially toward the uterus, enters at the level of the internal cervical os as a Gartner's duct. The remnant tubule can be dilated to form a cystic structure at any given point. Microscopically, they are often small tubules lined by cuboidal or columnar epithelium and surrounded by smooth muscle.
Paramesonephric cysts tend to be more laterally situated (whereas mesonephric cysts are closer to the uterus). Hydatids of Morgagni are the most common examples of this group and are usually located close to the fimbriated end of the fallopian tube. They are often lined by tubal-type epithelium.
Very common as an incidental finding during surgery for other reasons. Rarely, the cyst may become enlarged and be picked up on an annual exam.
Treatment is accomplished surgically via cystectomy or salpingectomy.
Few paratubal cysts enlarge to the point they require treatment and there is no risk of malignant conversion. If a cyst does significantly enlarge, it can cause pain as well as fallopian tube torsion and necrosis.
1 Robboy SJ, Anderson MC, Russell P. Pathology of the Female Reproductive Tract. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2002: 439-440.
2 Mills, S. Histology for Pathologists. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2007: 1055.
3 Mills SE, ed. Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincoott Williams & Wilkins; 2009: 2378.