
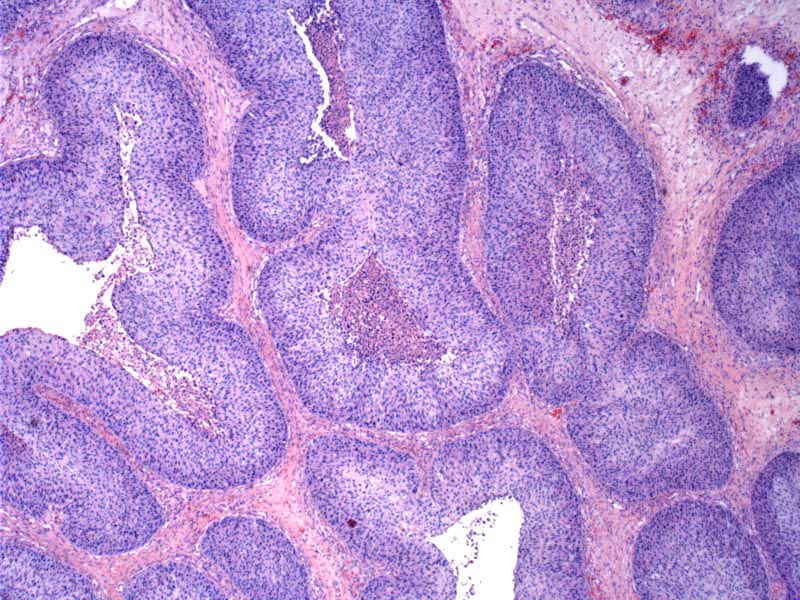
Case 1: Inverted pattern of growth, with dilated duct-like structures lined by a thick layer of epithelial cells. The surface layer consists of ciliated columnar epithelium with other types (squamous, ciliated columnar, transitional type) of epithelial cells underneath. Interspersed mucus-secreting cells may be found.
The inverted nature of the growth is quite obvious in this lesion.
Normal appearing epithelium covers the lesion; some stromal edema and mild inflammation are present.
Case 2: An inverted Schneiderian papilloma with low grade dysplasia.
Case 3: Inverted schneiderian papilloma with high grade dysplasia.
Case 4: This example arose shows larger and smaller inverted structures. Note the oncocytic epithelium.
This case actually can be designated as the oncocytic subtype. Some consider oncocytic SPs to be a variant of the inverted subtype, however most experts now place oncocytic SPs in its own category. Oncocytic SPs have no gender predilection and no association with HPV.
The inverted schneiderian papilloma most commonly occurs on the lateral nasal wall and often extend into the maxillary and ethmoid sinuses. Approximately 8% arise in the nasal septum and rarely, cases have been described in the middle-ear, pharynx, nasopharynx and lacrimal sac (Barnes).
About 38% of cases are associated with HPV subtypes 6 and 11, and less commonly HPV 16 and 18. association with an invasive carcinoma. Malignant transformation has been reported in 2-27% of studies in the literature (Barnes). The most common transformation is into a squamous cell carcinoma, but mucoepidermoid carcinoma, small cell carcinoma and sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma have also been reported.
These tumors tend to be unilateral, and present with nasal obstruction, epistaxis, headaches and anosmia. There is a male predilection with an age range of 40-70 years (Fletcher).
Recurrence rate of up to 75% if treated by local excision alone; lateral rhinotomy and medial maxillectomy are recommended, especially associated with a carcinoma (Mills).
→Male predilection; usually arises in the lateral nasal wall.
→38% of cases are associated with HPV; risk of malignant transformation.
• Sinonasal : Schneiderian Papilloma, Oncocytic Type
• Sinonasal : Schneiderian Papilloma with Dysplasia
• Ear : Inverted Schneiderian Papilloma
• Sinonasal : Respiratory Epithelial Adenomatoid Hamartoma
Barnes L. Schneiderian Papillomas and Nonsalivary Glandular Neoplasms of the Head and Neck. Mod Pathol 2002;15(3):279-297.
Fletcher CDM, ed. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2007: 83-7.
Mills SE, Gaffey MJ and Frierson HF. Tumors of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract and Ear, Atlas of Tumor Pathology. AFIP Third Series, Fascicle 26 (2000); 21-26.