
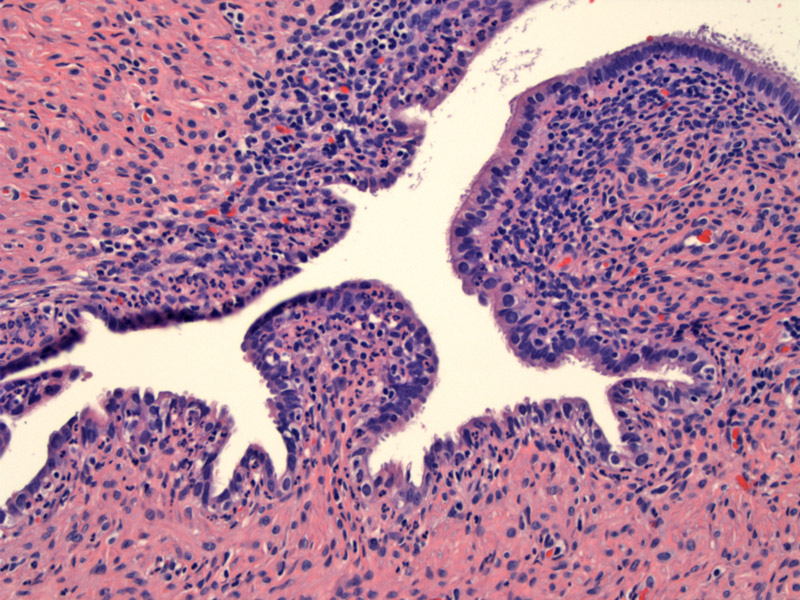
Neutrophils are found throughout the epithelium of the fallopian tube wall.
Extensive neutrophilic involvement of the surface tubal epithelium is present.
Acute salpingitis is classically a part of pelvic inflammatory disease, a polymicrobial infection ascending from the vagina through the uterus and fallopian tubes usually following in the wake of a gonococcal or chlamydial infection. Patients present with increased white blood cell counts, fevers, and pelvic pain.
Treatment is with broad spectrum antibiotics to cover the polymicrobial infection as well as the gonorrhea or chlamydia that likely preceded it. It has been safely shown that in the absence of sepsis or pelvic abscesses, these infections can be safely treated on an outpatient basis.
While most infections resolve with therapy, long term complications such as chronic pelvic pain and infertility are prevalent.
• Fallopian Tube : Tubo-ovarian Abscess