
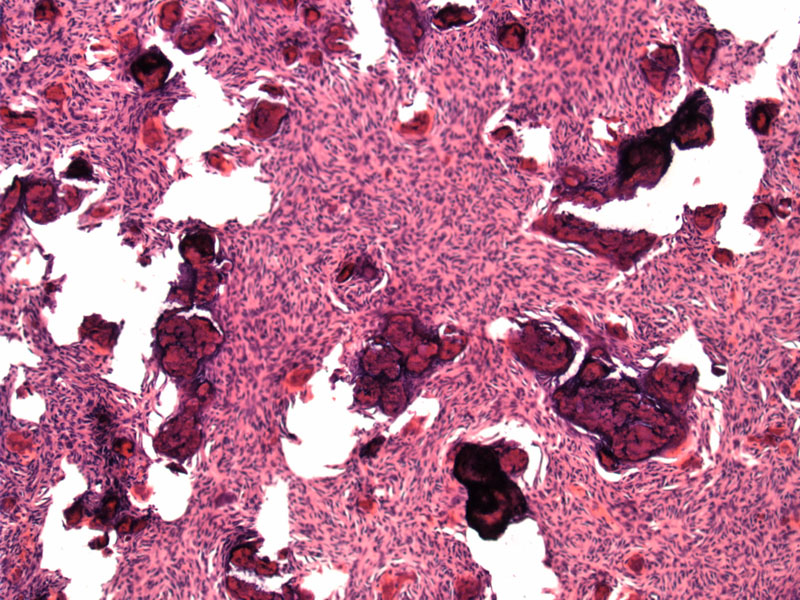
Case 1: Small ossicles are scattered heavily in a spindled cellular stroma.
The ossicles (cementicles) are spherical, resembling psammomatoid calcifications.
Juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibroma (a.k.a. juvenile active ossifying fibroma) is a specific subtype of ossifying fibroma distinguished because of its age predilection, site involvement, and clinical behavior.
JPOF tends to arise in younger patients and 90% arise in the sinonasal cavity, with the maxilla being the second most common location. Histologically, JPOF is composed of fibrous tissue and numerous psammomatous cementicles (ossicles). There may be osteoblastic rimming.
Of note, the other subtype of ossifying fibroma is juvenile trabecular ossifying fibroma (JTOF) has is composed of anastomosing bands of osteoid, as well as connecting cords/trabeculae of immature bone lined by plump osteoblasts. There are no psammomatoid ossicles in this variant.
JPOF affects a wide age range (3 months to 72 years) with a mean age of 15-20. The trabecular type, however, affects even a younger age (mean age of 8-12 years)(Barnes).
Complete surgical excision is recommended if feasible. If incompletely resected, may recur in up 1/3 to 1/2 of cases (Thompson).
• Oral Cavity : Ossifying Fibroma