System: Bone: Chondroid: Neoplastic: Chondrosarcoma, Myxoid Type

System: Bone: Chondroid: Neoplastic: Chondrosarcoma, Myxoid Type


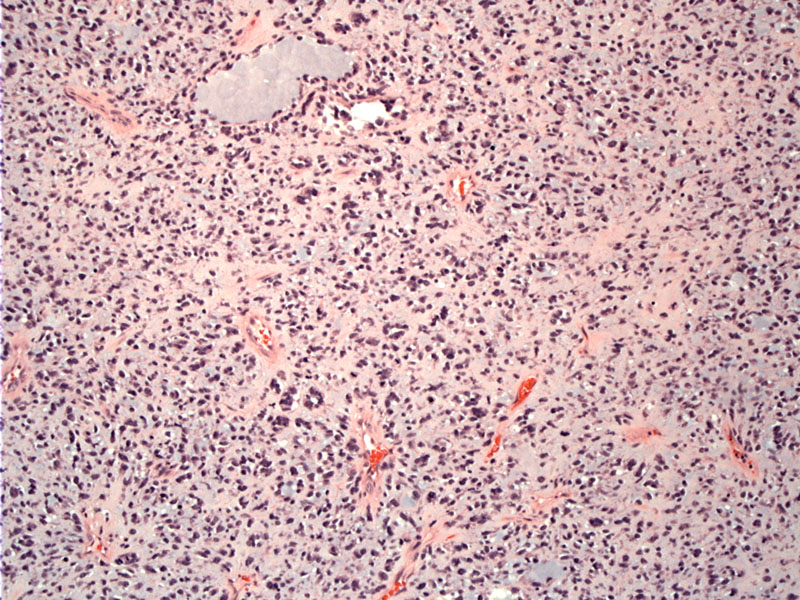
Tumor cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm consistent with chondroblasts are set in a myxoid stroma.
The tumor cells form a few clusters and but do not arrange in obvious cords or strands.
Primary skeletal mxyoid chondrosarcoma (SMC) can either describe a conventional chondrosarcoma with prominent myxoid stroma OR a distinctive myxoid sarcoma also known as "chordoid sarcoma" or "extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC)". If an EMC occurs within the bone, the terminology can be really confusing i.e. extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the bone or worse, intraosseous extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma. Obviously, these tumors are ridiculous.
EMC are predominantly located in the deep soft tissues and only rarely arise in the bone. SMC is usually in the bone and rarely arise in the soft tissues. Furthermore, EMC exhibit a characteristic translocation t(9;22) resulting in EWS-CHN fusion gene (Hisaoka).
In SMC, there is a nodular arrangment of tumor lobules. The individual neoplastic chondrocytes are separated by abundant mxyoid stroma. In EMC, a nodular architecture is also present due to increased cellularity at the periphery of the lobules. In contrast to SMC, in EMC the tumor cells are often clustered, arranged in cords or strands. The stroma is also myxoid (Antonescu).
Obviously, the microscopic features of SMC and EMC are not strikingly different, therefore, when in doubt, you should probably FISH for the translocation typical of EMC.
Of note, extraosseous chondrosarcomas in general are quite rare and are usually either EMC or the mesenchymal subtype.
In a comparison of 20 SMCs and 20 EMCs, the mean age for SMC patients was 45 and mean age for EMC patients was 55 (Antonescu).
→If one uses the general term skeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, beware. It can mean either conventional type chondrosarcoma with myxoid features or a specific soft tissue sarcoma with a characteristic translocation.
→Distinguishing between SMC and EMC is very difficult microscopically. In general, the tumor cells of EMC form structures (i.e. cords, strands, anastamosing cords, clusters) whereas in SMC, the tumor cells are more individual.
• Chondroid : Chondrosarcoma, Conventional Type
• Chondroid : Chondrosarcoma, Mesenchymal Type
• Chondroid : Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma
• Uncertain Lineage : Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma
Antonescu CR, et al. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma: A Comparative Clinicopathologic, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Study. Cancer 1998;83:1504-21.
Hisaoka M et al. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma: Updated clinicopathological and molecular genetic characteristics. Pathology International 2005;55:453-463.