
Islands of odontogenic epithelium are embedded in a loose stroma. Note the presence of amorphous material that may be enamel or dentin.
Thin cords of odontogenic epithelium embedded in a primitive ectomesenchyme; this area is indistinguishable from ameloblastic fibroma.
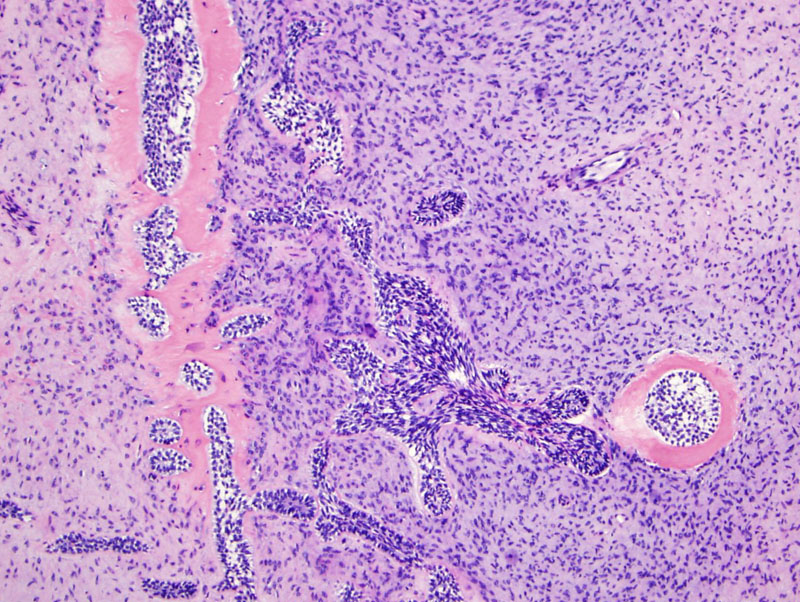
Another image with the components of odontogentic epithelium, mesechyme and dentin or enamel material.
The calcified material approximates the odontogenic epithelium.
The mesenchymal component is likened to dental papillae of developing teeth.
The odontogentic epithelium has two layers, an outer layer with darker basaloid cells that resemble ameloblasts and an inner loose layer that resembles stellate reticulum.
This second case also consists of anastamosing cords of odontogenic epithelium in a loose stroma.
The odontogenic epithelium can form islands, cords or strands.
Note the presence of dentin or enamel matrix next to the odontogentic epithelium.
Short cords of odontogenic epithelium within a loose myxoid stroma. Both components are bland, without atypia or hypercellularity.
Ameloblastic fibroma (AF) and ameloblastic fibro-odontoma (AFO) are related neoplasms composed of odontogenic epithelium and mesenchyme; fibro-odontomas have the added components of dentin and enamel.
Histologically, ameloblastic fibromas are composed of cords, strands and islands of odontogenic epithelium embedded in a loose stroma that resembles embryonic dental pulp. The palisading peripheral cells in the epithelial islands are basaloid and resemble ameloblasts -- whereas the central cells are looser and resemble reticulum-like tissue. In ameloblastic fibro-odontomas, mineralized material (enamel, dentin) is also present in the stroma (Barnes, Thompson).
These are uncommon tumors that occur within the first two decades of life (mean age between 8-12). AFOs are often asymptomatic, and often associated with an unerupted tooth. Ameloblastic fibromas have a slight male predilection whereas ameloblastic fibro-odontomas have equal gender distribution. The posterior mandible is the most common location.
Radiographically, there is a well-circumscribed unilocular or multilocular lucent area with areas of opacity (depending on the extent of mineralization).
A subset of ameloblastic fibromas do occur and uncommonly, may transform into ameloblastic fibrosarcomas. Ameloblastic fibro-odontomas, however, are not known to recur.
→Ameloblastic fibroma, ameloblastic fibrodentinoma and ameloblastic fibro-odontomas are related entities composed of amelolastic epithelium embedded in a loose pulp-like stroma.
→These are rare entities that arising mostly in young individuals, between age 8-12.
• Oral Cavity : Ameloblastic Fibroma
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. WHO Classification: Pathology and Genetics, Head and Neck Tumors Lyons, France: IARC; 2005: 308-9.
Thompson LDR, Wenig BM, eds. Diagnosis Pathology: Head and Neck. 1st Ed. Manitoba, Canada; Amirsys;2011; 6-48,49.